Amongst the participants hospitalized with COVID-19 we report that a higher prevalence of detectable SARS-CoV-2 plasma viral load is associated with worse respiratory disease severity lower. The most important take-home message is that a positive COVID-19 test by any method does not correspond to the presence of a viable virus.
COVID-19 Vaccine Reduces Severity Length Viral Load for Those Who Still Get Infected.

Covid 19 viral load and severity of illness. However the severity of and recovery from these symptoms have no correlations with the viral load of SARS-CoV-2. Our best belief is that the viral load and transmission peaks relatively early in the course of symptomatic disease and that by day 8 or 9 transmission risk is rapidly approaching baseline. Gregory Bix were among a group of scientists who co-authored a review to identify gaps in.
As researchers try to understand why some people infected with COVID-19 experience mild or nonexistent symptoms while others require hospitalization one factor they have considered is the. Once the COVID-19 virus enters a persons body it makes it the host and starts replicating fast inside the cells of that persons body. 4 Laryngoscope 1302680-2685 2020.
This studys objective was thus to explore whether a correlation exists between COVID-19 viral loads as indicated by RT-PCR Ct values and disease severity as indicated by respiratory indices. Currently our understanding of the relationship between viral RNA load kinetics and disease severity in patients with COVID-19 remains fragmented. Viral load is a measure of the.
Viral load refers to the amount of virus that can be detected in an infected person. Coronavirus disease 2019 COVID-19 is a new pandemic disease. A study on COVID-19 patients in China links high viral load to worse symptoms Viral load is the amount of a virus inside someones body.
People with COVID-19 who continue to show a high viral load seem to have more serious symptoms. These symptoms may get worse if you. A multi-centre cross-sectional retrospective study was conducted using data obtained from Bahrains National COVID-19 Task forces centralised database.
There is a high prevalence of olfactory and gustatory dysfunction in COVID-19. In this study of patients with COVID-19 across a wide spectrum of severity we observed that viral shedding in the respiratory tract lasting longer than 14 days was common. And a growing cohort of coronavirus survivors called long-haulers has reported symptoms and side effects including fatigue impaired memory and heart problems that can linger for months.
In humans randomised trials of patients with viral upper respiratory tract infections have shown mask wearing reduces viral droplet emissions14 Furthermore masks have been found to reduce inhalation of particles15 Several epidemiological studies have indicated mask wearing and other social distancing measures reduce the severity of covid-1916 17. Viral load peaked later in the second week of illness in more severe disease. Real-world data from the AZ HEROES study show COVID-19 vaccines are highly effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infections and when breakthrough infections do occur the level of infection and impact of the disease are significantly reduced.
While experts believe there is evidence that viral load could indicate how severe COVID-19 could be they also dont think its the only factor that contributes to severe illness. Collectively these data from different cohort of patients suggests that severe COVID-19 patients with a high viral load correlate with higher risk for severe infection with ICU admission and multi-organ dysfunction. High viral loads are concerning because they can mean the person is more infectious.
The initial dose of virus and the amount of virus an individual has at any one time might worsen the severity of COVID 19 disease. We previously reported that the viral load of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SARS-CoV-2 peaks within the first week of disease onset12 Findings from Feb 2020 indicated that the clinical spectrum of this disease can be very heterogeneous3 Here we report the viral RNA. Compared to an initial low viral load a high initial viral load was an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality OR 55 CI 3197 p 0001 and intubation OR 182 CI 107311 p 003 while an initial intermediate viral load was associated with increased risk of inpatient mortality OR 19 CI 114321 p 0015 but not.
Amongst the participants hospitalized with COVID-19 we report that a higher prevalence of detectable SARS-CoV-2 plasma viral load is associated with worse respiratory disease severity lower absolute lymphocyte counts and increased markers of inflammation including C-reactive protein and IL-6. Seem to show that a higher viral load makes coronavirus symptoms worse. As viral loads go down their chances of getting better go up.
What is the meaning of the term Viral Load in COVID-19. Viral load in COVID-19 is associated with transmission risk and disease severity as in any other viral illnesses. Zou and colleagues reported that patients with COVID-19 with more severe disease requiring intensive care unit admission had high viral RNA loads at 10 days and beyond after symptom onset.
Breakthrough infection refers to cases in which a person vaccinated against COVID-19 nonetheless becomes infected with the virus. Factors common to these cohorts was increased age and active preexisting medical co-morbidities. The relationship between viral dose and COVID-19 severity.
There is a long list of medical conditions that can increase the chances of having a severe case of COVID-19 from diabetes to high blood pressure. It is known to be a contributing factor to severe illness and death among COVID-19. Tulane researchers Chad Roy PhD and Dr.
However a study of patients hospitalised with covid-19 in Nanchang China found a strong association between disease severity and the amount of virus present in the nose.

Inoculum At The Time Of Sars Cov 2 Exposure And Risk Of Disease Severity International Journal Of Infectious Diseases

Viral Dynamics Of Sars Cov 2 Across A Spectrum Of Disease Severity In Covid 19 Journal Of Infection
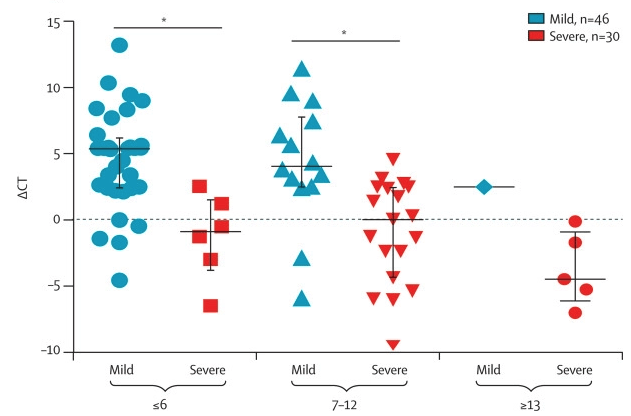
Viral Dynamics Mild Vs Severe Covid 19 Immunopaedia

The Kinetics Of Viral Load And Antibodies To Sars Cov 2 Clinical Microbiology And Infection

Increased Viral Variants In Children And Young Adults With Impaired Humoral Immunity And Persistent Sars Cov 2 Infection A Consecutive Case Series Ebiomedicine
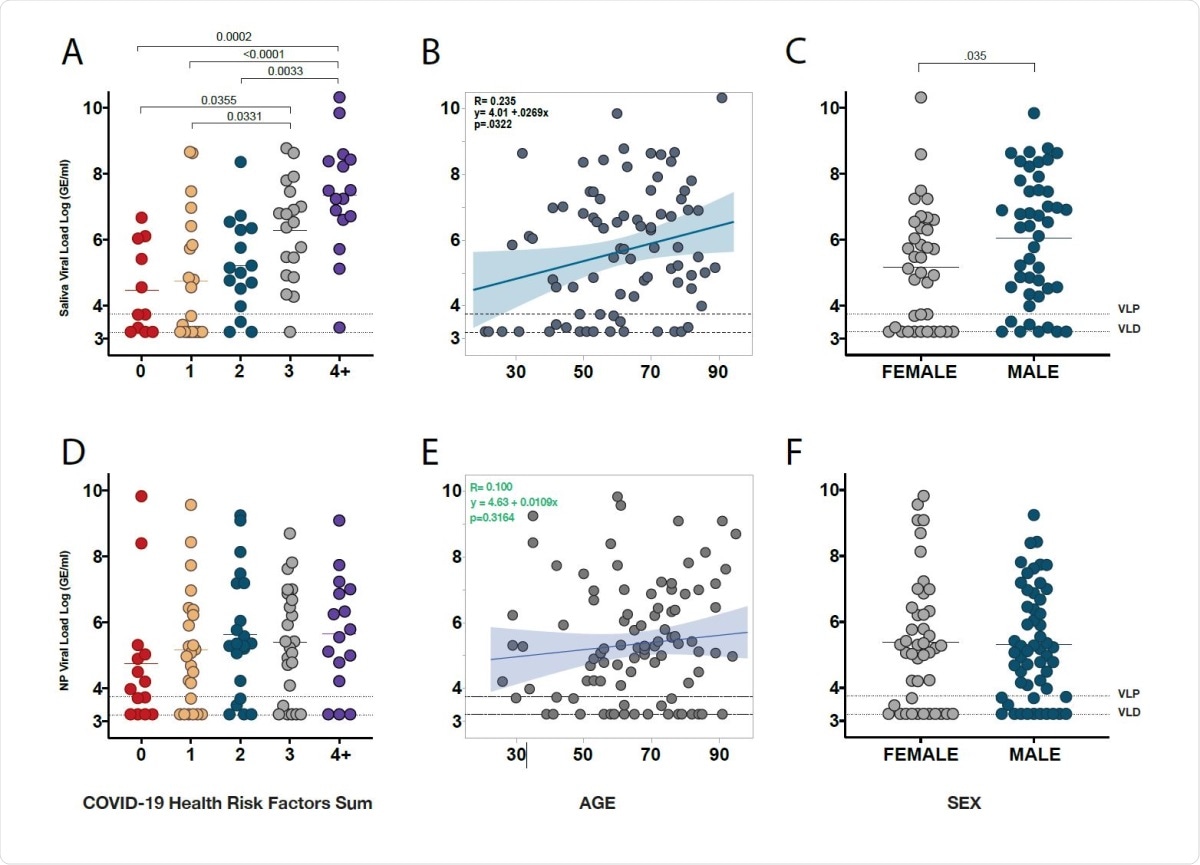
Sars Cov 2 Viral Load In Saliva May Be Linked To Covid 19 Disease Severity

Pathogenesis Of Covid 19 Induced Ards Implications For An Aging Population European Respiratory Society
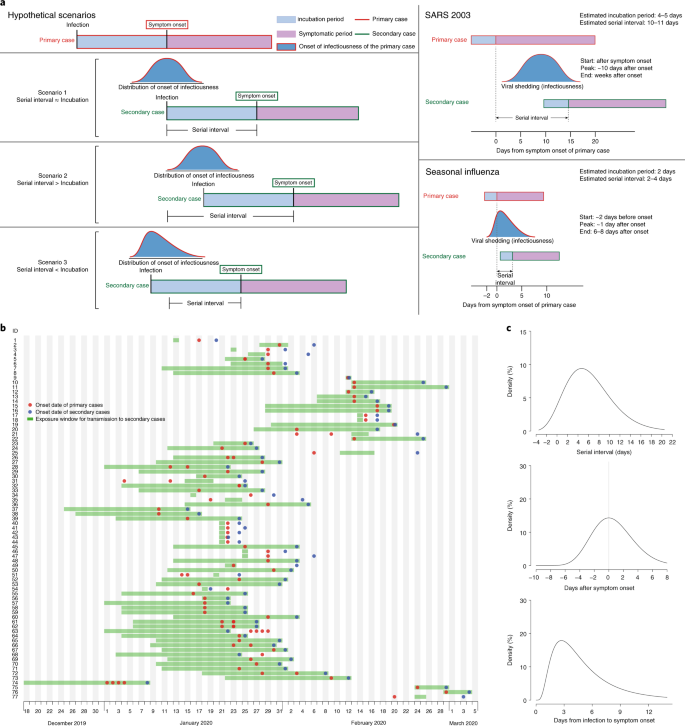
Temporal Dynamics In Viral Shedding And Transmissibility Of Covid 19 Nature Medicine
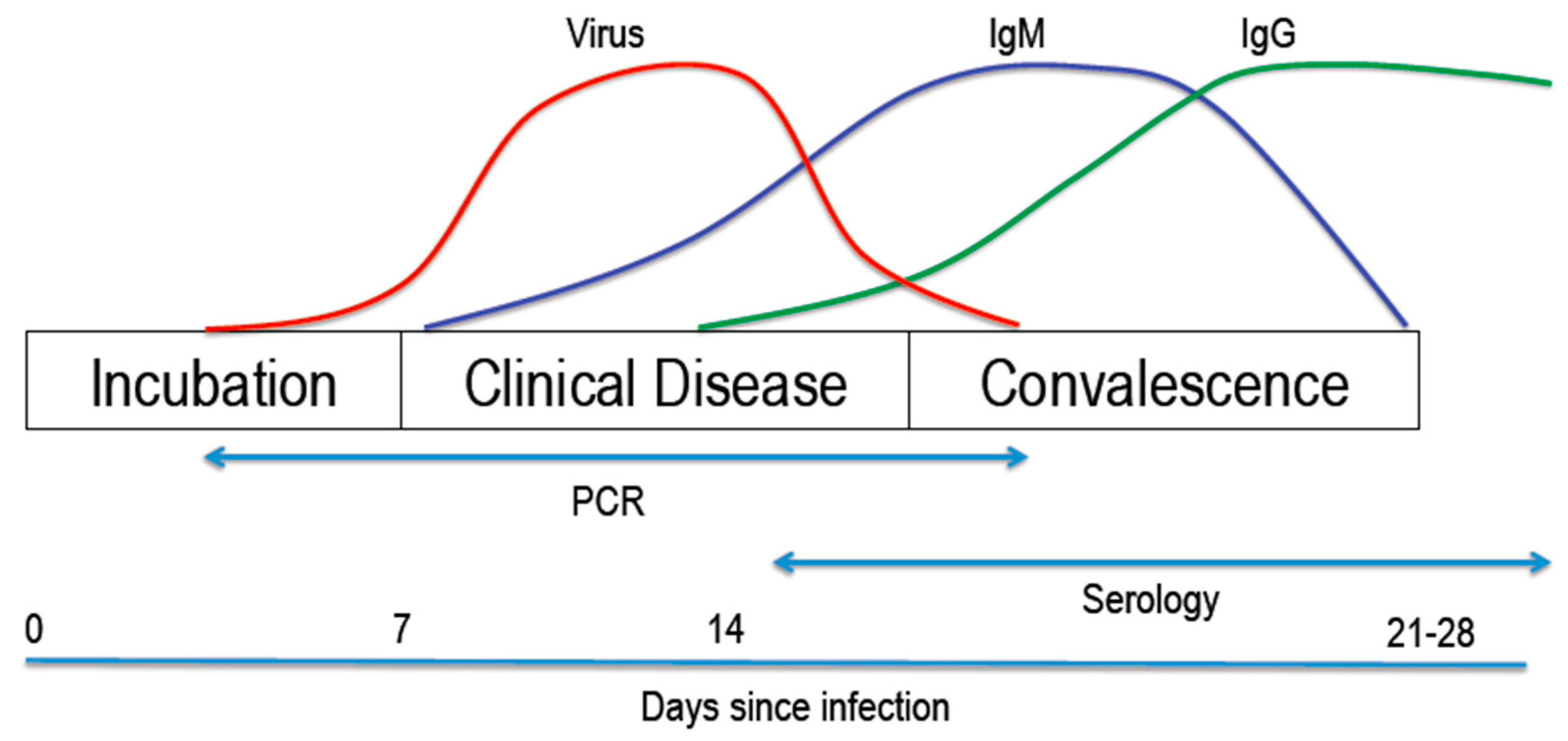
Jcm Free Full Text Update For Anaesthetists On Clinical Features Of Covid 19 Patients And Relevant Management Html

Charting A Coronavirus Infection The New York Times

Saliva Viral Load Is A Dynamic Unifying Correlate Of Covid 19 Severity And Mortality Medrxiv
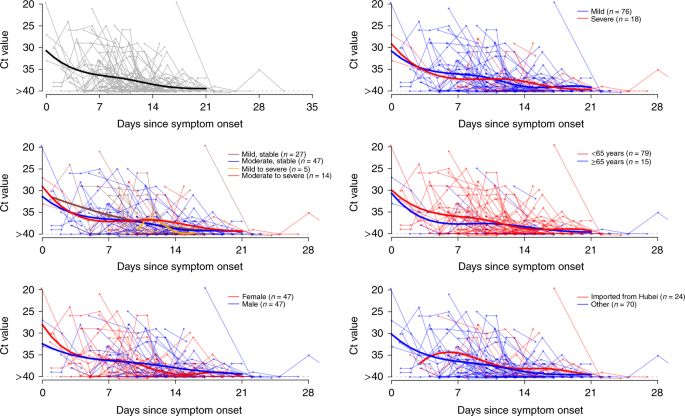
Temporal Dynamics In Viral Shedding And Transmissibility Of Covid 19 Nature Medicine

Sars Cov 2 Viral Loads Of Exhaled Breath And Oronasopharyngeal Specimens In Hospitalized Patients With Covid 19 International Journal Of Infectious Diseases

Sars Cov 2 Viral Load Peaks Prior To Symptom Onset A Systematic Review And Individual Pooled Analysis Of Coronavirus Viral Load From 66 Studies Medrxiv

Does A High Viral Load Or Infectious Dose Make Covid 19 Worse New Scientist

Virology Transmission And Pathogenesis Of Sars Cov 2 The Bmj Du Cote De La Science

Dynamics Of Sars Cov 2 Shedding In The Respiratory Tract Depends On The Severity Of Disease In Covid 19 Patients European Respiratory Society
Covid 19 And Sars Cov 2 Immune Response Mechanistic Insights World Allergy Organization

Frontiers Sars Cov 2 Viral Load Is Correlated With The Disease Severity And Mortality In Patients With Cancer Oncology
Comments